
How To Make Sure That Your Company Is GDPR Compliant
|
There isn’t one easy fix to become GDPR compliant. Almost all organizations handle some form of personal data, and many employees are required to handle personal data daily. Therefore, it is important to have a clear set of guidelines and to make sure that everyone knows what to do. Which is why we believe it is important to train your team through awareness training. Here you find a list of things to help make sure that your company is on the right track. If you don’t follow the GDPR it might result in huge fines – the maximum fine is 20 million € or 4% of your global annual revenue.
Table of content
-
Your company must be aware of the GDPR rules
-
Make sure you know who is responsible – it could be a Data Protection Officer (DPO)
-
Your whole team must know how to handle personal data
-
Create clear guidelines to make sure the GDPR rules are followed
-
Do a risk analysis to figure out what’s next
-
Create a good process for working with GDPR with the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle
-
You could get certified to prove compliance
-
Security breaches are often human breaches
-
Avoid penalties and fines
-
Data protection is an ongoing process
-
Have an eye on GDPR rulings – the guidelines are constantly evolving
Your company must be aware of the GDPR rules
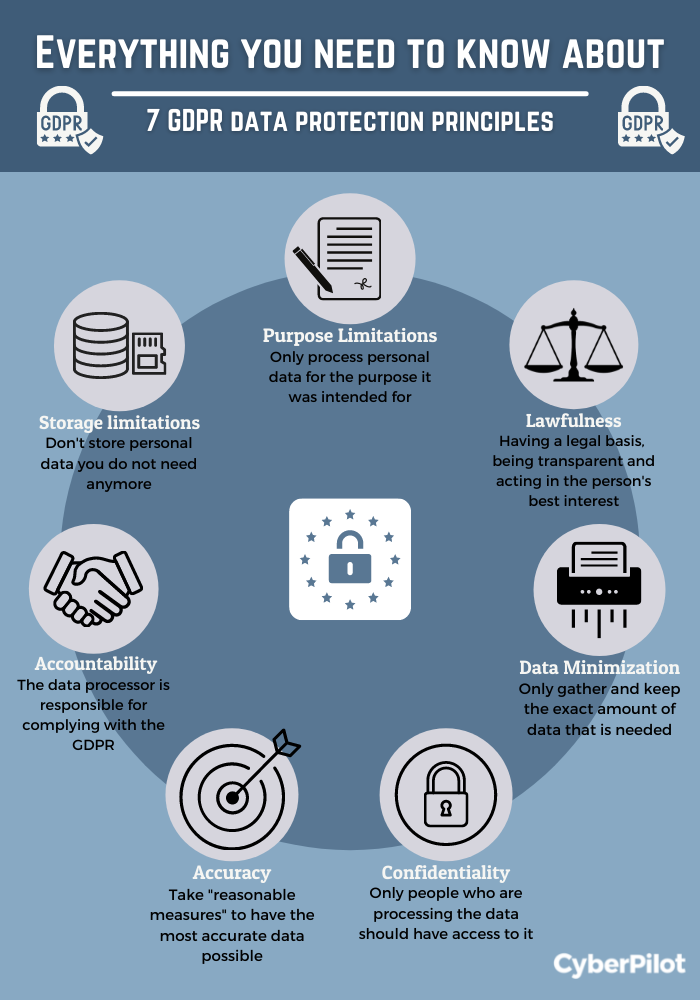
The first step to becoming GDPR compliant is to make sure that someone in your company understands what the GDPR is all about. The GDPR is built on 7 principles which can be used as a foundation to understand why and how personal data should be handled. The principles are used to highlight the main idea behind GDPR and to uncover some of the methods that can help you in your daily tasks such as data minimisation.
It also underlines the importance of having a lawful basis to handling personal data which means you must have a valid reason to process people's personal data, and this can be done through consent as you often see on websites.
Now you must take these principles and put them into action.
It can be challenging to achieve goals and implement the 7 principles if there isn't a designated person or team who is responsible for making the organization GDPR compliant.
Although your colleagues are the ones, who are handling personal data day-to-day, it is still important to have someone who is responsible for making sure that everyone knows what to do and that this person is the one to turn to when in doubt. The responsibility can be shared by a team, in small companies it can be one of the leaders responsibility or it may well be a Data Protection Officer (DPO) who’s task it is to advice the company on GDPR, that will ensure that the company is GDPR compliant
There isn’t a one size fits all solution as it depends on the organizational structure in your company. It may be a little excessive to have a designated DPO in a small start-up, but there is also a possibility that it could become unclear who should do what if the responsibility is shared by too many. It is also possible to outsource the role to an external company. The key is that you all agree on who is in charge regarding GDPR and your employees know who to ask when they have questions.
Your whole team must know how to handle personal data
Knowing who is responsible for the GDPR in your company is not enough on its own as all your employees will individually handle personal data to some degree. Therefore, it is important that everyone in the organization has a basic understanding of how personal data should be handled.
This is not to say that everyone needs to be an expert, however it is important that your employees have a good understanding of what personal data is and how to handle it securely. Below are some examples of things your employees should know:
-
What is personal data
-
What is considered as sensitive personal data
-
Whether or not you have a legal basis for processing personal data
-
How the different types of personal data should be handled
-
What to do if you spot a data breach
-
Who to ask for help when in doubt
There are many ways to raise awareness and educate your team members around data handling. Seminars, courses and awareness training are all great ways to make sure that everyone has a strong understanding of secure data handling. It is important to remember why education around data handling must be seen as a priority since mistakes made by employees are still one of the most common reasons behind data breaches.
| The 8 basic rights of the GDPR of Data Subjects (the user) |
The GDPR will make sure that we live up to the data subjects' rights. Here is a short description of the 8 rights every individual has. |
|
1. The right to access |
This means that every individual has the right to request access to their personal data. They also have the right to know how the organization is using it. |
|
2. The right to be forgotten |
This means that consumers can require to have their personal data deleted if they no longer consent or if they are no longer customers. |
|
3. The right to data portability |
Individuals have the right to transfer their data from one service provider to another service provider. |
|
4. The right to be informed |
Individuals must be informed about data being collected and they must have the option of opting in and out. |
|
5. The right to have information corrected |
All individuals have the right to have their data updated if it is incorrect, incomplete or out of date. |
|
6. The right to restrict processing |
All individuals have the right to restrict processing. This means that they can choose to allow companies to use data for some but not all purposes. |
|
7. The right to object |
All individuals have the right to object and demand that companies and public authorities stop using their data without explicit consent e.g., for direct marketing. |
|
8. The right to be notified |
If a data breach is likely to result in a high risk, the data subject has the right to be notified without undue delay. |
The importance of delegating responsibly and educating your team on data handling is crucial and therefore must be done as soon as possible. Additionally, a way to help your team is by creating clear guidelines on data handling, this is something your team can easily access when unsure about unfamiliar situations. Having a clear set of guidelines also ensures that processes around data security are streamlined throughout your organization. As a result, the guidelines can help make your cyber security stronger and reduce the risk of facing security and data breaches.
Let's dive into some of the documents and guidelines you could create for your company.
Creating an IT Security Policy makes sure that your company has a general framework around how to work with cyber security. It sets several objectives. It also points out who is responsible for achieving these objectives and who is responsible for the overall cyber security work. The policy is made at a strategic level, and it sets the tone for the cyber security work in your organization which also helps prevent data breaches. You can check out our free template and guide on how to make a IT security policy.
Acceptable Use Policy – create concrete and actionable rules and guidelines
As mentioned earlier, the IT Security Policy is the strategic framework for the cyber security and protection of personal data, whereas the Acceptable Use police is more practical and actionable hence the name. It is the document you can use to put your objectives into practice through guidelines and rules that your employees can follow. It is important to remember that the list of rules must not be excessively long and complex as this can result in employees becoming demotivated, which would be counterproductive. The Acceptable Use Policy should be easy to understand, follow and must align with your end goal of strengthening cyber security within your organization. We have a free template and guide on how to make an Acceptable Use Policy.
|
What is Personal data? |
|
Personal data is information that can be used to identify a specific person. It includes information such as name, address, license plate, a job application, or a picture of a tattoo. If personal data is categorized as sensitive the GDPR requires a higher level of security. |
|
General Personal data |
| - Name |
|
- Mobile number |
|
- Date of birth |
|
- Occupation |
|
- Address |
|
Sensitive personal data |
|
- Race or ethnic origin |
|
- Political or religious beliefs |
|
- Trade union membership |
|
- Genetic data / biometric data (e.g., fingerprints) |
|
- Health information |
| - Sexual relationships or orientation |
Do a risk analysis to figure out what’s next
What’s next?
The vague but correct answer is: It depends.
All companies are different, it's impossible to say what you should do now. What your next move should be depends on several factors including the type of data you process, the systems you are using and what the potential consequences would be if there were to be a security breach.
To make an informed decision about your next steps, it may be a good idea to do a risk analysis to get a better understanding of what your organisation needs regarding security and protection. A risk analysis aims to give an overview of the types of threats your organization may be susceptible to, it also estimates the likelihood of threats and what the consequences of such threats may be for your organization.
Naturally, threats which are more likely to occur and that could potentially be more harmful should be dealt with first. Threats could range anything from your employees clicking on phishing links to sending sensitive personal data to someone who shouldn’t receive it. You can use our free risk analysis template to map out all of your company threats.
Be aware that the risk analysis process is not performed in the same way under the ISO-standards as under GDPR.
Create a good process for working with GDPR with the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle
As you might have already guessed, the GDPR is not a quick fix task but an ongoing process. You are never entirely done as new challenges will continue to arise overtime. You cannot expect to simply present your team with rules, expect that they follow them perfectly each time and for it to be a smooth process from there on. It is important that you have a good process in place which allows you to assess, evaluate and adjust the systems and guidelines as needed. This will help make your data processing smoother and more secure over time.
One way of doing this is to use the Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle (PDCA) which is an iterative method that makes sure:
-
You create a set of goals and a plan on how to reach them
-
You follow the plan and do the work
-
You evaluate the work to see if you reached your goals
-
You act on the result to make sure you keep improving
You could get certified to prove compliance
When it comes to GDPR and you are a data processer, a key thing to remember is that the data controller must audit you. This means you are required to formally document that you are processing personal data in accordance with the GDPR. Often this results in having to deal with a great deal of queries back and forth which can prove to be time-consuming.
If this continues to be an inconvenience for you, it may be worth getting certified or getting a security audit. Both can be a way of showing that you are committed to good practice when it comes to information security and data handling. This may not be for everyone as it can be relatively expensive to get certified and audited, and it requires a great deal of work therefore you should thoroughly consider whether it is right for you while at the same time following the GDPR.
A lot of certifications and reports to choose from
There are many certifications and standards to consider when it comes to GDPR and cyber security work. Some are GDPR-specific while others are not but can still be useful.
Below is a list of certifications you may want to consider:
-
ISAE 3000 GDPR report
-
ISO 27701 certification
-
ISAE 3402 report
-
ISO 27001 certification
They can all be used to show GDPR-compliance, but they are not the same.
ISAE 3000 is often used in GDPR
One way to use auditor statements or certifications in your GDPR work is to get an ISAE 3000 auditor statement also called an ISAE 3000 GDPR report/statement. Its purpose is to assess whether you live up to the responsibility of being a data processor. If you get audited and receive the ISAE 3000 statement you can show this to data controllers which will help to prove that you process personal data as required by the rules.
ISO 27701 is a new certification created for the GDPR
In 2019 the international ISO-organisation presented a new standard: the ISO 27701. Many are familiar with the ISO 27001, which will be further explained in the next section, but the ISO 27701 is a new certification.
The not-so-catchy name for the certification is “Security techniques – Extension to ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/ 27002 for privacy information – Requirements and guidelines”.
The certification covers whether you are compliant with the GDPR. So, on paper, it sounds like the perfect certification for all of us. But the fact is that the certification is still fairly new, and we need to see how it performs in practice before making any conclusions. It could end up being a mixture between the ISAE 3000 and ISO 27701 which is needed but we are still learning as we go.
You could get ISO 27001 certified or ISAE 3402 security audited
Despite ISAE 3000 being the most GDPR-specific report and ISO 27701 the most GDPR specific certification, many are looking towards the ISAE 3402 and ISO 27001. The ISAE 3402 is a thorough declaration which focuses on reporting and financial transactions and is often used to make sure the daily operations and deliveries in IT are being carried out safe and sound – And for this reason it can be used for GDPR and cyber security as well. ISAE 3402 is based on the framework ISO 27001. The ISO 27001 is a standard which helps companies secure valuable and personal data. The goal is to create strong information security.
As this is quite a heavy topic let's not burden you with the in-depth knowledge here. Instead, you can take a look at our comprehensive guide on ISO 27001 and ISAE 3402 and what to consider before diving into it with a splash.
ISAE 3000 vs. ISAE 3402
Okay, but what is the difference between the two and why are people using both? Well… The short answer is that the ISAE 3000 is typically about data and how to protect it which is why it fits the scope of the GDPR.
The ISAE 3402 on the other hand is about processes and physical conditions. It’s about making sure that there is no downtime on servers, backups are in place if data is deleted and that there are procedures for when it comes to operations such as backups, logging, power etc. It can also play an important part in securing personal data; however, it has a much larger scope than that.
Security breaches are often human breaches
Data breaches do occasionally happen. We are all human and humans make mistakes especially when in a hurry or not fully aware of the impact of our actions. Statistics from the Danish Data Protection Agency(Datatilsynet) shows that one of the most common GDPR and security breaches are emails being sent to the wrong recipient.
A seemingly small mistake but a security breach nonetheless, as personal data could end up in the wrong hands when sent to the wrong people who should not process or have access to it under any circumstance.
This underlines not only the importance of making sure that team members are aware of risks involved when handling data, but also how difficult It is to avoid data breaches. One of our core goals as a cyber security company is to reduce the number of security breaches caused by employees which is why we so heavily focus on awareness training and phishing training.
The basis of all of this people-centered work is having a strong security culture, which is the foundation of a secure organisation. You can read our guide on how to develop and maintain a strong security culture in your organisation.
Avoid penalties and fines
There are a great deal of rules and regulations to follow when managing a security breach however one of the first things to remember when a security breach occurs, is to document the breach and notify your local supervisory authority no later than 72 hours after the breach was spotted. You must have a valid reason to not have notified them within 72 hours. Most security breaches are not serious enough by nature to lead to fines and penalties. If you as an organization have the correct processes in place and generally do your best to protect personal data, you may not have much to worry about. Alternatively, if you haven't taken the initiative to follow the GDPR and are not aware of guidelines around data security, you may end up in a situation which is less than ideal. The level of security needed when dealing with lawsuits is something which we are still learning about as things are continually evolving and the rules tend to vary from country to country. Reading and learning more about the kind of data breaches that are fined, can help you set the level for your GDPR work.
Data protection is an ongoing process
As we have discussed, being GDPR compliant is not as simple as it may seem. There is no plug and play solution to becoming GDPR compliant. The steps given above should help you get started with figuring out what the options for your organization are, but it is important to understand that becoming GDPR compliant is an ongoing process and that challenges differ from company to company. It is natural to become tired and overwhelmed trying to solve everything all at once so try instead to take it step-by-step.
Start with the most impactful thing you can do, and then work your way through it.
Have an eye on GDPR rulings – the guidelines are constantly evolving
Lastly, we would like to point out the importance of keeping an eye on all the rulings we see about the GDPR. Even though it has been around since 2018 it is still a new regulation, so the field is constantly evolving as we saw with the Schrems II ruling that made the Privacy Shield Framework no longer a valid basis for processing personal information in the United States. We had to wait an entire year for new recommendations on how to transfer personal data to third-party countries.
Does it sound like a tough job keeping up with all the GDPR rulings? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. If you sign up to our newsletter, we promise to update you on the most important GDPR related news and other cyber security related topics.
You will receive inspiration, tools and stories about good cyber security practice directly in your inbox. Our newsletter is sent out approximately once a month.






