CIS Controls V8: What Is CIS 18 And How To Use It For Awareness Training
The Center for Internet Security released an updated version of security safeguards in 2021, called the CIS Controls v8. It’s made up of 18 controls (so it’s also called CIS 18) which can be implemented by any organization to enhance their security against the most common cybersecurity threats.
In this blog post, we give you a general overview of the CIS Controls v8 with a deep dive on Control 14, which requires security awareness training. Continuous security awareness training is the best way to establish a strong security culture. It teaches your colleagues about security threats so they can defend your organization against cyberattacks. Because training is so important (and it’s our focus here at CyberPilot), we mostly discuss Control 14. We provide suggestions for how you can achieve all implementation guidelines for Control 14 and show you how our security awareness and phishing training checks all the boxes.
Is CIS 18 relevant for my organization?
There are a lot of cybersecurity frameworks and policies out there, and most organizations work with a few different variations. For instance, you might work with both the GDPR and ISO 27001 or other frameworks related to specific countries and industries.
CIS Controls Version 8 serves as an optional best practice guide that some organizations use to strengthen their security and prioritize their IT investments. It’s popular because it gives you actionable steps to take to protect your organization from some of the most common cybersecurity threats. In fact, a lot of our customers already use or are considering using CIS Controls v8 to keep their security in tip top shape. So, we’ve made a short introduction to the CIS 18 framework and how we can help you achieve compliance with Control 14. Take a look and see if the CIS Controls could be something for your organization to use!
CIS 18 is the newest version of CIS Controls
CIS Controls Version 8 is the most recent list of security safeguards published by the Center for Internet Security (CIS), a non-profit that has been issuing world-renowned security recommendations for over twenty years. Together, the controls provide a list of best practices that organizations can use to guide their IT security work by protecting themselves against the most common cybersecurity threats, like phishing and malware.
CIS Controls v8 has been around since 2021, and it replaced CIS Controls v7. The newer version gives organizations 18 critical security controls to work with instead of the 20 that were included in CIS Controls Version 7. The controls and implementation guidelines are free to access, so any organization can use them to improve its cybersecurity.
The image below shows the updated 18 CIS Controls in v8 and how these new controls compare to the 20 controls in v7.
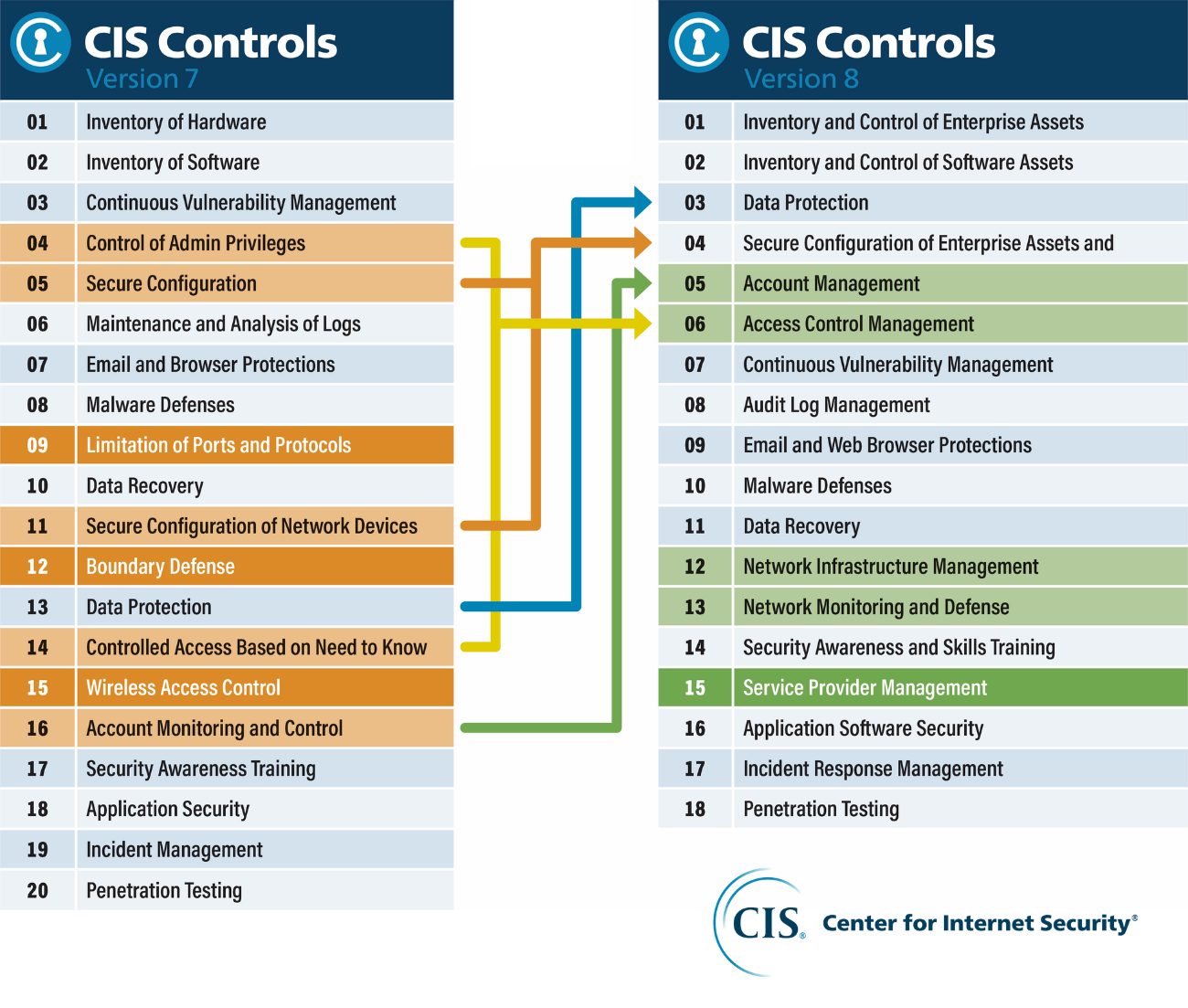
Source: https://www.cisecurity.org/controls/v8
CIS Controls v8 is made up of 18 controls
The 18 controls in Version 8 give you 18 different categories of actions that make up a strong security system. Each control has an overall goal with a list of implementation guidelines that CIS recommends in order to reach that goal. Essentially, the guidelines give you a checklist of best practices that will help you achieve the overall goal of the control. The more guidelines you implement across the different controls, the stronger your security will become.
Each of the CIS 18 controls is listed here, with a link to CIS’ overview of the control.
- CIS Control 1: Inventory and Control of Enterprise Assets
- CIS Control 2: Inventory and Control of Software Assets
- CIS Control 3: Data Protection
- CIS Control 4: Secure Configuration of Enterprise Assets and Software
- CIS Control 5: Account Management
- CIS Control 6: Access Control Management
- CIS Control 7: Continuous Vulnerability Management
- CIS Control 8: Audit Log Management
- CIS Control 9: Email and Web Browser Protections
- CIS Control 10: Malware Defenses
- CIS Control 11: Data Recovery
- CIS Control 12: Network Infrastructure Management
- CIS Control 13: Network Monitoring and Defense
- CIS Control 14: Security Awareness and Skills Training
- CIS Control 15: Service Provider Management
- CIS Control 16: Application Software Security
- CIS Control 17: Incident Response Management
- CIS Control 18: Penetration Testing
Since the 18 CIS controls cover so many different parts of an organization’s security, from sophisticated technological defenses to internal preparation and planning, it’s hard to tackle each of the controls at once. It’s less overwhelming to focus on one control at a time and create a plan around how you will work to implement that control. You’ll probably find that you will rely on different services and experts in your work towards achieving different controls.
Here at CyberPilot, we are all about training. We focus on security awareness training because we know that human error is behind most IT security incidents. We also know that by providing continuous training and fostering a strong security culture, it’s possible to reduce the risk of a security breach within your organization.
So in the next sections, we’ll talk about CIS Control 14 and what it says about security awareness training.
Exploring Control 14: The security awareness and skills training guidelines of CIS Controls v8
If you just read the overview of Control 14 provided by CIS, you will find a vague requirement to have a continuous security awareness training program. Here is what Control 14 states:
“Establish and maintain a security awareness program to influence behavior among the workforce to be security conscious and properly skilled to reduce cybersecurity risks to the enterprise."
The reason for this control, according to CIS is that there is no security program that can eliminate our human vulnerabilities:
“The actions of people play a critical part in the success or failure of an enterprise’s security program. It is easier for an attacker to entice a user to click a link or open an email attachment to install malware in order to get into an enterprise, than to find a network exploit to do it directly. Users themselves, both intentionally and unintentionally, can cause incidents.”
Sure, regularly training your organization on security risks is a great goal to have. But how do you make it happen?
The implementation guidelines provided by CIS are a good place to start. They give you nine different best practices to help you create and maintain a successful security awareness training program. Here are the 9 recommendations:
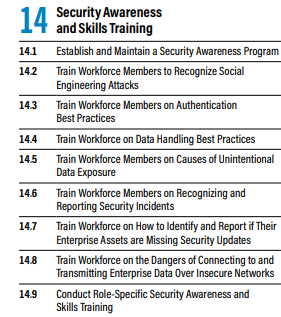
Source: https://www.cisecurity.org/controls/v8, CIS Controls v8 Implementation Groups
We’ll dive deeper into each of the nine recommendations next, giving you actionable steps to meet each guideline.
14.1 Establish and Maintain a Security Awareness Program
The first step is to create and maintain a security awareness training program, which makes sense as the rest of the best practices are about characteristics that your training program should have. If you don’t already have an IT security training program in place, getting started can seem overwhelming.
There are a lot of decisions to make when you’re first deciding what your security awareness training program should look like.
- What should your awareness training cover and how should you implement it?
- How do you make security awareness training interesting so people actually pay attention?
- Should you do your training with online courses, in person meetings, or a combination of both?
In addition to cybersecurity best practices, it’s also important to train your colleagues on the IT security and data protection laws in your country, like the GDPR. Although it seems like a lot to cover, regulations and best practices often overlap, because they work towards the same goal – better security and data protection. This means that tying the topics together will require a little thought, but the content will blend together seamlessly.
Maintaining the security awareness training program is important so that good digital habits are always fresh in your colleagues’ minds. We recommend a format of learning called microlearning, which gives lessons in small doses over a long period of time. This is a natural way to keep and maintain a training program since you’ll have new topics to cover every couple of months. We use it in our own training program too, where we release new 5-7 minute courses every other month.
14.2 Train Workforce Members to Recognize Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks like phishing are the biggest security threat that organizations face today. If we aren’t diligent and aware, we can easily fall for a social engineering attack and compromise passwords, bank account details, or access to IT systems.
For this reason, training your colleagues on how to recognize these kinds of attacks is critical. The best way to teach your team about social engineering is by exposing them to different tactics. One effective way to teach your colleagues to recognize social engineering is by running phishing simulations. Simulations work so well because they give your colleagues exposure to what a realistic threat could look like, so they know exactly what to be on guard for in their everyday work. Simulations have an added bonus of giving you real-time insights into how your colleagues perform, letting you know how well your team can detect social engineering threats and whether they report them correctly.
We have a guide to help you get started with phishing simulations, where we talk about how often you should send fake phishing emails, and common issues you might experience when teaching your employees about phishing, and how to overcome them.
Combine phishing testing with awareness training courses for the best outcome
In addition to practical phishing tests, it’s helpful to give your colleagues awareness training courses that teach them about how to detect phishing emails and commonly used social engineering tactics. That way, your team can become familiar with the lessons about how to spot a phishing email and then put their skills to the test during a phishing simulation. Our guide on designing a training program with social engineering and phishing courses can give you inspiration for topics to cover in your training. Another helpful resource could be our course specifically on social engineering.
14.3 Train Workforce Members on Authentication Best Practices
Once your team knows the basics, like how to make a strong password and how to detect a phishing email, it’s time to take their skills to the next step. Authentication is a way to validate a user’s identity. In IT security, authentication is important for accessing accounts and double-checking that an email requesting sensitive information is legitimate.
So, for authentication best practices, we advise training your employees about two-factor authentication – how it works and why they should use it on their accounts.
We also suggest that all organizations create a culture where it is acceptable to authenticate the origin of emails before taking action. For instance, if you get an email from your coworker asking you to share a password, you should contact that person another way (by talking to them in person or giving them a call) to make sure the request is legitimate before acting. This is an important way to detect and prevent phishing attacks.

14.4 Train Workforce on Data Handling Best Practices
Training your colleagues on the proper handling of personal data could be important for your organization because of GDPR compliance, limiting data breaches, or just following security best practices. Handling data is most likely part of everyone’s job description. It has to be done carefully in order to protect an individual’s privacy and protect people from fraud in the case of data breaches.
A few data handling topics you might train your employees on could be:
- What personal data is
- The legal requirements for processing personal data
- Who should have access to personal data
- How to minimize the amount of data you store, and why you should
- How to securely get rid of data when you no longer need it
Maybe it’s also relevant for your colleagues to know about what a data processor and data controller are. By training your team about good habits when handling data, you can greatly minimize the risk of something going wrong with a data breach or a GDPR violation.
14.5 Train Workforce Members on Causes of Unintentional Data Exposure
Most security incidents happen by accident. For example, we might accidentally send an email with data to the wrong person, post something online without realizing it has personal data in it, or share the wrong tab for everyone to see during a video meeting.
It could also happen that you’re sitting in a café and don’t realize that the person sitting next to you has a clear view of your screen, which has your clients’ data displayed. The bottom line is that most security incidents are caused by human error. And the first step towards preventing these mistakes is to be aware of them. Training your colleagues on the various ways they might accidentally expose data will help them slow down and be careful when accessing personal data.
14.6 Train Workforce Members on Recognizing and Reporting Security Incidents
We train so that we are prepared for the real deal when it happens. By teaching your organization how to recognize a potential security issue and the correct reporting process, you ensure that they will be ready to act during a real breach. Again, this is where a combination of security awareness training and phishing testing is useful.
You can first teach your team about the signs of a breach and what to do if they suspect a security incident. The response process could be, e.g., “Do not open any links or download any attachments. Contact the head of IT immediately and then warn your colleagues.”
After teaching your team about the signs of a breach and the reporting process, you can test how they respond to a security incident in practice with a phishing simulation. This kind of practical exercise will tell you where you should focus your future training, based on two insights. First, you’ll see how well your team can detect a security incident based on the number of people who take the desired action in the phishing email. Second, you’ll also get an idea of how well your colleagues understand the reporting process based on how many people contact the correct (or incorrect) person. Both of these insights will help you figure out if there is any confusion that you should clarify in future trainings.
14.7 Train Workforce on How to Identify and Report if Their Enterprise Assets are Missing Security Updates
Security updates are something we all get every few months or so. And because we get them so often, and usually have to restart our devices to complete them, it’s tempting to put them off. This can become a problem when we keep hitting the “remind me tomorrow” button instead of installing the update.
The problem is that most people don’t realize how important these updates are. They repair bugs and security vulnerabilities in software, so postponing an update is sort of like leaving the window to your house open while you’re on holiday.
We suggest teaching your colleagues all about security updates, including why they should keep their devices up to date and how to check if an update is available.
14.8 Train Workforce on the Dangers of Connecting to and Transmitting Enterprise Data Over Insecure Networks
Working from a café, hotel, or on public transport is quite common. And many people connect to the free Wi-Fi offered in these locations without thinking twice about it. But even though free Wi-Fi is convenient, it’s also unprotected and dangerous. When Wi-Fi is unprotected, cybercriminals can lurk on the network and steal your data or put malware on your device. This kind of situation would be bad for your personal devices, but the consequences are even greater if you use a work device because you’re putting the data and systems of your entire company at risk.
That’s why it's important to educate your team on why they shouldn’t use public Wi-Fi and what they should use instead. For instance, instead of connecting to a hotel’s free internet when travelling, it’s a better idea to connect to a mobile hotspot. A mobile hotspot allows you to connect one device, e.g., a laptop, to the internet by using the mobile data of another device, like a cell phone. Since you’re connecting through one of your own devices, mobile hotspots are secure. We cover all of these topics in our course about working on the go.
14.9 Conduct Role-Specific Security Awareness and Skills Training
When you have your security awareness training program in place and you’ve covered the basics, you can start getting more in-depth with role specific training. Maybe learning about data processing agreements isn’t relevant for everyone, but it could be important for team leaders who manage contracts with external partners. It’s also possible that different departments in your organization don’t all use the same programs in their everyday work. The accounting team might use a billing system that nobody else touches, while the product team might use a tech platform that is specific to their work. In this case, you might want to customize your training to the software or platforms that are used by different departments so the training is relevant to the unique threats and programs they work with.
Research shows that you can increase information retention by making the training relevant to your colleagues. So every once in a while, see if you can tailor your security awareness training to the job descriptions of your colleagues.
CyberPilot’s security awareness training meets all implementation guidelines for Control 14
Now that we’ve gone step by step through how you could tackle each of the nine implementation guidelines in Control 14 of CIS 18, you should have a good idea of how to get started with your security awareness training. To make it even more clear, we’ll show you how CyberPilot can help you achieve all nine guidelines and help you achieve compliance with Control 14.
14.1 Establish and Maintain a Security Awareness Program
- CyberPilot’s security awareness training publishes new courses every two months (in addition to our catalogue of existing courses). This helps you to maintain a training program where your colleagues are kept up to date about new security threats. Try our courses for free for 14 days.
- CyberPilot’s Awareness Intro course gives an overview of why cyber security is more important than ever
14.2 Train Workforce Members to Recognize Social Engineering Attacks
- Our security awareness training provides many courses about how to recognize different types of phishing and social engineering tactics. For example, our courses on phishing and social engineering will give your colleagues an introduction to the topics.
- You can expand upon the introductory courses with more in-depth courses, like our course on targeted (spear) phishing. Starting with the basics and then breaking down the topics further is a great way to maintain a training program with new content that will develop your colleagues’ knowledge over time.
14.3 Train Workforce Members on Authentication Best Practices
- Authentication is an important layer of your organization’s defense against security threats. And there are different types of authentication. For instance, you can teach your colleagues about how and why they should use two factor authentication on their accounts with our course on two factor authentication. This kind of authentication verifies a person’s identity when accessing an account.
- Another type of authentication is how we verify that emails are legitimate and coming from who they claim to be. This kind of authentication protects your organization against phishing attempts, because it requires your colleagues to confirm that an email with sensitive data requests is legitimate before performing an action. In our course on how to handle a phishing email, we go over ways to authenticate emails, such as talking to the sender in person or calling them.
14.4 Train Workforce on Data Handling Best Practices
- Data handling best practices are important if your organization needs to comply with the GDPR. When your employees handle data with care, they also help your organization prevent costly data breaches.
- We have several courses that will train your employees about what personal data is and precautions they should take when handling it. For example, we have courses that cover the legal grounds for processing data and how to protect personal data.
14.5 Train Workforce Members on Causes of Unintentional Data Exposure
- Nobody would intentionally expose sensitive data (except for cybercriminals). Yet it happens all the time – little mistakes that are easy to make when we aren’t paying attention can lead to big data breaches. That’s why training your team about how they might accidentally expose data is important. It’ll show them why they should always be aware of potential security risks.
- To help you, CyberPilot has a course about email and personal data, since sending personal data over email is one of the biggest sources of unintentional data exposure. We also have a course about security risks to be aware of during video meetings, as accidentally sharing the wrong screen can display sensitive data to the incorrect audience.
14.6 Train Workforce Members on Recognizing and Reporting Security Incidents
- Since our colleagues are our first line of defense against security breaches, it’s crucial that they know how to recognize and correctly report a potential security threat. Our course on CEO fraud can make your team aware of this dangerous security threat, while our course on how to handle a phishing email will give practical steps to take when exposed to a security incident. You should also clearly communicate your organization’s unique reporting process to everyone.
- To train your employees on reporting security incidents and test their preparedness, we advise sending simulated phishing emails through a phishing training program. This will give your team the opportunity to put what they’ve learned through training courses into practice.
14.7 Train Workforce on How to Identify and Report if Their Enterprise Assets are Missing Security Updates
- Updates are an often-overlooked part of IT security. But they shouldn’t be! Installing updates on our devices when they become available patches holes in their security and makes them less vulnerable to malicious cyberattacks.
- To train your colleagues about the importance of installing updates in a timely manner, we have a course about updates. We also cover updates along with other topics in our course about protecting your work computer.
14.8 Train Workforce on the Dangers of Connecting to and Transmitting Enterprise Data Over Insecure Networks
- Insecure networks are something we all need to be careful about, especially since many of us work in places like cafes, hotels, or public transportation. However, the dangers of connecting to public or insecure networks are not well known, which can cause major security risks.
- With CyberPilot’s awarenss training, we have several courses that will prepare your colleagues to practice good digital habits while working away from the office or their home. For example, we have a course about safe surfing on the internet and another course about working on the go. These courses will teach your colleagues to think twice before using public Wi-Fi and what to do instead.
14.9 Conduct Role-Specific Security Awareness and Skills Training
- With CyberPilot’s awareness training, you can send courses to certain people or teams –this is useful when there is a topic that you want one team to get a refresher or more detailed information on.
- You can also create your own courses using CyberPilot’s platform. By tailoring your courses, you can cover topics specific to the duties and tools used by each team.
So that’s it! Hopefully you now have a good idea of how CyberPilot can help you comply with every part of Control 14 in CIS Controls v8. We’ve got it all covered, with the courses we listed above and many more. And with new courses coming out every other month, you can be sure that our security awareness training will keep your team aware and secure.
CIS Controls v8 is one of many cybersecurity frameworks you can use
There are a lot of different cybersecurity frameworks you can work within, and CIS Controls v8 is just one of them. Some other frameworks are the GDPR, ISAE 3000, ISAE 3402, ISO 27001, and NIS2. We won’t get into all of them here, but in this post we break down common cybersecurity policies and frameworks, and what each of them require for security awareness training.
The framework that you work within will depend on your industry, location, and where you do business. Many of the frameworks overlap and help you work towards GDPR compliance too.
If you are curious for more information, this page has information on how the CIS Controls help you comply with other security frameworks, including the GDPR, NIST, and ISO 27001.
Security awareness training helps you meet the CIS 18 standards while improving your overall security
The updated CIS Controls demonstrate just how important it is to train your organization in IT security best practices. Continued security awareness training is required as a part of the CIS Controls v8 and other security regulations, like the GDPR. It’s required because it works!
CyberPilot’s security awareness training and phishing testing are two ways to meet these security awareness training requirements and prepare your organization for the most common security threats. If you are interested in learning more about how we can partner to suport your organization’s cybersecurity compliance, please feel free to contact our team.
You will receive inspiration, tools and stories about good cyber security practice directly in your inbox. Our newsletter is sent out approximately once a month.